For example, often only the liabilities accounts that are actually labelled as “debt” on the balance sheet are used in the numerator, instead of the broader category of “total liabilities”. The current ratio measures the capacity of a company to pay its short-term obligations in a year or less. Analysts and investors compare the current assets of a company to its current liabilities. Many companies borrow money to maintain business operations — making it a typical practice for many businesses.
Q. Are there any limitations to using the debt to equity ratio?
For example, Company A has quick assets of $20,000 and current liabilities of $18,000. Quick assets are those most liquid current assets that can quickly be converted into cash. These assets include cash and cash equivalents, marketable securities, and net accounts receivable.
- These can include industry averages, the S&P 500 average, or the D/E ratio of a competitor.
- Including preferred stock in total debt will increase the D/E ratio and make a company look riskier.
- It is a measure of the degree to which a company is financing its operations with debt rather than its own resources.
- Using the D/E ratio to assess a company’s financial leverage may not be accurate if the company has an aggressive growth strategy.
- Therefore, this includes all of the company’s debt with a maturity of more than one year.
Using the Debt-to-Equity Ratio for Personal Finances
A high D/E ratio suggests that the company is sourcing more of its business operations by borrowing money, which may subject the company to potential risks if debt levels are too high. If earnings don’t outpace the debt’s cost, then shareholders may lose and stock prices may fall. A debt-to-equity-ratio that’s high compared to others in a company’s given industry may indicate that that company is overleveraged and in a precarious position. The debt-to-equity ratio is most useful when used to compare direct competitors.
Get in Touch With a Financial Advisor
This is a significant jump from the 3.9% rate the company had previously been paying. Currency fluctuations can affect the ratio for companies operating in multiple countries. It’s advisable to back to basics: bookkeeping terms every small business owner should know consider currency-adjusted figures for a more accurate assessment. For the remainder of the forecast, the short-term debt will grow by $2m each year, while the long-term debt will grow by $5m.
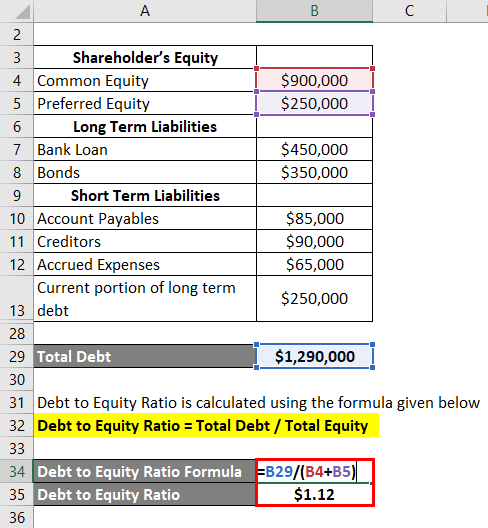
How to Calculate the Debt-to-Equity Ratio
In the financial industry (particularly banking), a similar concept is equity to total assets (or equity to risk-weighted assets), otherwise known as capital adequacy. Gearing ratios are financial ratios that indicate how a company is using its leverage. As an example, the furnishings company Ethan Allen (ETD) is a competitor to Restoration Hardware. The 10-K filing for Ethan Allen, in thousands, lists total liabilities as $312,572 and total shareholders’ equity as $407,323, which results in a D/E ratio of 0.76. For growing companies, the D/E ratio indicates how much of the company’s growth is fueled by debt, which investors can then use as a risk measurement tool.
Limitations of the D/E Ratio
But a D/E ratio above 2.0 — i.e., more than $2 of debt for every dollar of equity — could be a red flag. Again, context is everything and the D/E ratio is only one indicator of a company’s health. Debt-to-equity ratio is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to evaluating stocks. Whether the ratio is high or low is not the bottom line of whether one should invest in a company. A deeper dive into a company’s financial structure can paint a fuller picture.
In order to calculate the debt-to-equity ratio, you need to understand both components. For example, utility companies have highly reliable sources of revenue because they provide a necessary commodity and often have limited competition. This allows companies to take on greater debt without taking on greater risk. Newell Brands, the maker of Sharpies and Rubbermaid containers, refinanced $1.1 billion in bonds in September 2022, agreeing to an interest rate of 6.4–6.6%.
Another popular iteration of the ratio is the long-term-debt-to-equity ratio which uses only long-term debt in the numerator instead of total debt or total liabilities. This second classification of short-term debt is carved out of long-term debt and is reclassified as a current liability called current portion of long-term debt (or a similar name). The remaining long-term debt is used in the numerator of the long-term-debt-to-equity ratio. It shows the proportion to which a company is able to finance its operations via debt rather than its own resources. It is also a long-term risk assessment of the capital structure of a company and provides insight over time into its growth strategy.

This is beneficial to investors if leverage generates more income than the cost of the debt. By learning to calculate and interpret this ratio, and by considering the industry context and the company’s financial approach, you equip yourself to make smarter financial decisions. Whether evaluating investment options or weighing business risks, the debt to equity ratio is an essential piece of the puzzle.